For two or three years Mary had known that her memory was slipping. First she had trouble remembering the names of her friends’ children, and one year she completely forgot the strawberry preserves she had put up.
▶ She compensated by writing things down. After all, she told herself, she was getting older. But then she would find herself groping for a word she had always known, and she worried that she was getting senile.
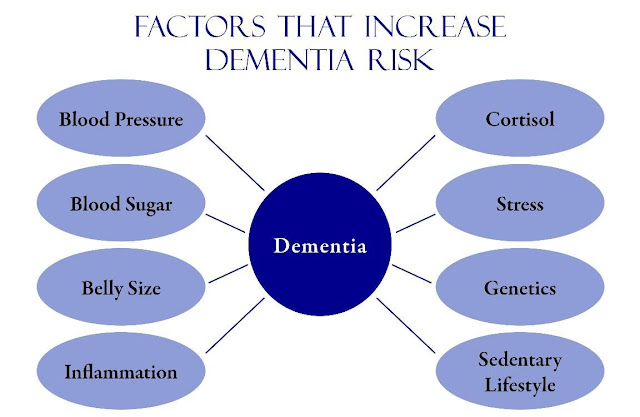
✔ WHAT IS DEMENTIA ?
You may have heard different terms for the symptoms of forgetfulness and loss of the ability to reason and think clearly. You may have been told that the person has "dementia" or "Alzheimer's." You may also have heard the terms ‘‘organic brain syndrome," "hardening of the arteries," or "chronic brain syndrome." You may have wondered how these conditions are different from "senility."
Doctors use the word dementia in a special way. Dementia does not mean crazy. It has been chosen by the medical profession as the least offensive and most accurate term to describe this group of illnesses. Dementia describes a group of symptoms and is not the name of a disease or diseases that cause the symptoms.
✔ Whats the Major Conditions ?
There are two major conditions that result in the symptoms of mental confusion, memory loss, disorientation, intellectual impairment, or similar problems. These two conditions may look similar to the casual observer and can be confused.
The first is dementia. The second condition, delirium, Delirium is important to you because occasionally a treatable delirium will be mistaken for a dementia. Sometimes people with Alzheimer disease or another dementia develop a delirium and have symptoms that are worse than the dementia alone would cause.
✔ The symptoms of Dementia - The Best Part :
The symptoms of dementia can be caused by many different diseases. Some of these diseases are treatable, others are not. Thyroid disease, for example, may cause a dementia that can be reversed with correction of a thyroid abnormality.
Alzheimer disease is the most frequent cause of irreversible dementia in adults. The intellectual impairment progresses gradually from forgetfulness to total disability. There are structural and chemical changes in the brains of people with Alzheimer disease.
At present, physicians know of no way to stop or cure it. However, much can be done to diminish the patient’s behavioral and emotional symptoms and to give the family a sense of control of the situation.
✔ The Person with Dementia :
Usually the symptoms of dementia appear gradually. Sometimes the afflicted person may be the first to notice something wrong. The person with a mild dementia is often able to describe his problem clearly: "Things just go out of my mind."
"I start to explain and then I just can’t find the words." Family members may not notice at first that something is wrong. The person with a dementia has difficulty remembering things, although he may be skillful at concealing this.
You may observe that his ability to understand, reason, and use good judgment may be impaired. The onset and the course of the condition depend on which disease caused the condition and on other factors, some of which are unknown to researchers. Sometimes the onset of the trouble is sudden: looking back, you may say, "After a certain time, Dad was never himself."
✔ How People Respond to their Problems ?
People respond to their problems in different ways:
- Some people become skillful at concealing the difficulty.
- Some keep lists to jog their memory.
- Some vehemently deny that anything is wrong or blame their problems on others.
- Some people become depressed or irritable when they realize that their memory is failing.
- Others remain outwardly cheerful.
What’s more ?
Usually, the person with a mild to moderate dementia is able to continue to do most of the things he has always done. Like a person with any other disease, he is able to participate in his treatment, family decisions, and planning for the future.